Density is defined as mass per unit volume and is expressed mathematically as d mV d is density m is mass and V is volume. These processes include Formation of the solar system Formation of compositional layers within the earth Convection currents within the outer core the asthenosphere the oceans and the atmosphere Subduction of crust through plate.

How To Find Density 8 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
Calculate the density by measuring the mass and volume of your samples.

. The diameter of the Earth at the equator. Determine the mass of the object. Dry density of soil is determined by first determining the in-situ density of soil and then calculating dry density by using the equation.
Experimentally mass and volume measurements are required to calculate density. Alternatively you can measure mass by using a balance. Place the object on an accurate scale and record the mass in your notebook.
Typically densities are reported gml or gcm 3 which are equivalent because 1ml 1cm 3. Design an experiment to test a hypothesis. Calculate the weight of packing material W P W TSP W T W S.
Calculate the density using the formulae and check your results in the respective space. Describe the procedure for determining the density of earth materials. Many of Earths processes are due to different densities of materials within the Earth.
Record your observation of measurement of mass and volume in the below tables as shown. Density ρ Mass M Volume V Density is an intensive property meaning it does not depend on the size of the object. 1 the subduction of more dense oceanic crust underneath continental crust.
This formula 43πr 3 requires the radius of the Earth. Calculate the volume of packing V P W P ρ P. And the sinking of colder lithospheric plates at subduction zones thus creating the conveyor belt model that somehow drives the plate tectonics engine.
For gravitational Mass of the Solid M Block. DENSITY The volume of a regularly shaped solid object such as sphere cylinder or cube can be found by. Things that are less dense will float and things that are more dense will sink.
The in-situ density is determined by the following methods. M moisture content or water content. Soil density plays a major role both in plant growth and in engineering uses of soil.
Water is an unusual earth material because it is densest in which phase. Method 1Method 1 of 2Measuring Density Directly. Compare the densities of different materials.
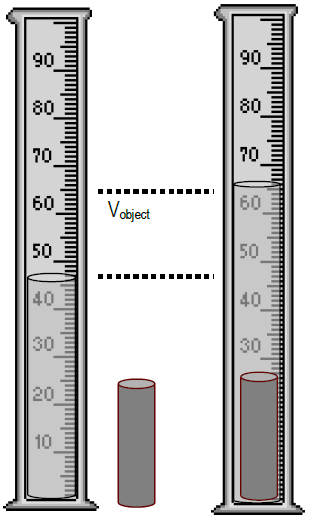
4 Using the method of water displacement determine the volume of all rock samples. Compare your results to those obtained by other groups for the. ρ P is the density of the packing material see below.
You can present this in various ways. In order to find the volume of the Earth you need more information than just the volume of a sphere formula. 3 the collision and uplift of continental crust at continent to continent.
2 the rising of hotter mantle material at divergent boundaries. Calculate the sample density ρ S W SV T V P. Up to 24 cash back To calculate density you divide the mass of the object by the volume of the object.
It is measured by weighing the object directly. Record your results in the table below. If you were to ignore the water what would be the effect on your density calculation.
I Sand replacement method. Density is essentially a measurement of how tightly matter is packed together. You will make this measurement three times and calculate the average.
Different materials can have different densities and density can be used to identify a substance. The density does not affect is the affection of pressure and temperature In other words at larger pressures and temperatures you get more density thats why the center of the earth is solid and its circundant cap is liquid cause in the center the extreme pressure compresses the atoms into the solid state and in the nearness which pressure is less it. For a gas which is much less dense the volume is usually in liters and its density is expressed as gL or g L-1.
This famous procedure is known as the Cavendish Experiment. Density is an important concept in a wide range of fields including chemistry physics material science. Density is defined as the ratio of the mass of an object to the volume it occupies.
The formulas for calculating bulk density and particle density follow. Density of Earth Materials Lab. Measure the mass of your samples using the triple beam balance provided.
Density an intensive or intrinsic property is a kind of heaviness factor. In macroscopic terms density reflects how much mass is packed into a given three-dimensional space. 2 Using the triple beam balance determine the mass of all rock samples.
Calculate the density of each liquid from the gradient of its graph line. Have students determine the scale and assemble their own columns have students determine the scale as you build the column use a 1000mL graduate or. G Bulk density or insite density.
There is water on the pan of the scale as you measure the mass of a mineral. How do your density data compare to your estimates of the relative densities of the minerals. Bulk density ρb mass of oven dry soil total soil volume Bulk density ρ b mass of oven dry soil total soil volume.
Up to 24 cash back 4. Prepare a density column see this 5 Layer Density Column Lab to model the density sorting of the interior of the Earth. Either sets of units are generally acceptable but all.
6 Determine the densities of the rock samples. 7 Answer provided questions. Where Y d dry density of soil.
Correspondingly he could then find the attraction on a mass the size of the Earth and then determine its density. 5 Record the volumes in the chart. Mass is the amount of matter in an object and its unit is grams.
3 Record these masses in the chart. Students will need to have studied density previously and be familiar with the density equation. Modeling the Density of the Earth with a Density Column.
Thus the density of a solid or liquid is expressed as grams per milliliters gmL or g mL1 or grams per cubic centimeters gcm3or g cm3. Yd Y1m. Identify and use laboratory equipment.
Explain density using examples. D MV where D density gmL M mass g and V volume mL. Obtain a set of objects cube cylinder sphere etc made of the same material.
Record the density of each sample on your chart in grams per milliliter gmL. 1 Obtain tray of materials. Picture 3 Density is important to us because it determines whether something sinks or floats.
Do the measurement a couple of times to make sure you really did fill all nooks and crannies with the beads the first time. Examples may have used cm 3 as the unit of volume and gcm 3 as the unit of density or m 3 and kgm 3. Written out the formula for calculating density is.

How To Find Density 8 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
Lab 1 Density Determinations And Various Methods To Measure Volume

To Determine The Density Of Solid By Using A Spring Balance And A Measuring Cylinder Lab Work
0 Comments